Quick Sort
Partition a Given Array
Input: arr[] = {13, 16, 22, 20, 17} pivot = 5 Output: arr[] = {13, 16, 17, 22, 20} or arr[] = {16, 13, 17, 22, 20} return value: 2 It is a new index of pivot element
Stability in Partition
├── Stable
│ └── Naive Partition
└── Not Stable
├── Lomuto Partition
└── Hoare's Partition
Naive Partition
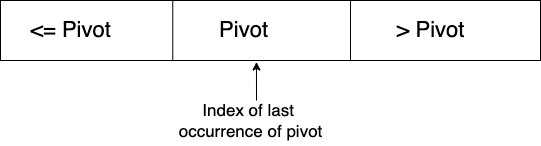
Input: arr[] = {12, 17, 18, 13, 17} pivot = 1 or 4 Output: arr[] = {12, 13, 17, 17, 18} return value = 3
Note: Please note in the return value on above example that we return the last index of 17 i.e. 3, even our pivot is 1 or 4. So we need to return the last occurrence of pivot element as explained in above example.
Implementation
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
arr := []int{30, 80, 40, 90, 10, 50, 70}
p := partition(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, len(arr)-1)
fmt.Println(p) // 4
fmt.Println(arr) // [30 40 10 50 70 80 90]
}
func partition(arr []int, l, h, p int) int {
temp := make([]int, h-l+1) // create temp array
idx := 0
for i := l; i <= h; i++ {
if arr[i] < arr[p] {
temp[idx] = arr[i] //Smaller in temp array
idx++
}
}
for i := l; i <= h; i++ {
if arr[i] == arr[p] {
temp[idx] = arr[i] // equal elements in temp. We could do thi sin first loop but we need this loop for stability
idx++
}
}
res := l + idx - 1 // last ocurrance of pivot
for i := l; i <= h; i++ {
if arr[i] > arr[p] {
temp[idx] = arr[i] // greator elements in temp
idx++
}
}
for i := l; i <= h; i++ {
arr[i] = temp[i] // copy to original array
}
return res
}
Complexity
Time Complexity: θ(n) Aux Space Complexity: θ(n)
Dry Run
arr[] = {5, 3, 12, 8, 5} l=0, h=4, p=0
After 1st loop temp[] = {3, , , , } After 2nd loop temp[] = {3, 5, 5, , } After 3nd loop temp[] = {3, 5, 5, 12, 8} After 4th loop arr[] = {3, 5, 5, 12, 8}
Lomuto Partition
arr[] = {10, 80, 30, 90, 40, 50, 70} l=0, h=6, pivot=70
Lomuto partition always selects the last element s pivot element.
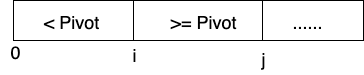
As above diagram explains, the Lomuto partition moves < pivot elements into 0 --> i section and keeps >=pivot elements intp i --> j section.
Implementation
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
arr := []int{30, 80, 10, 90, 40, 50, 70}
p := lomutoPartition(arr, 0, len(arr)-1)
fmt.Println(p)
fmt.Println(arr)
}
func lomutoPartition(arr []int, l, h int) int {
p := arr[h]
i := l - 1
for j := l; j < h; j++ {
if arr[j] < p {
i++
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
}
}
arr[i+1], arr[h] = arr[h], arr[i+1]
return i + 1
}
Complexity
Time Complexity: O(n) Aux Space Complexity: O(1)
Dry run
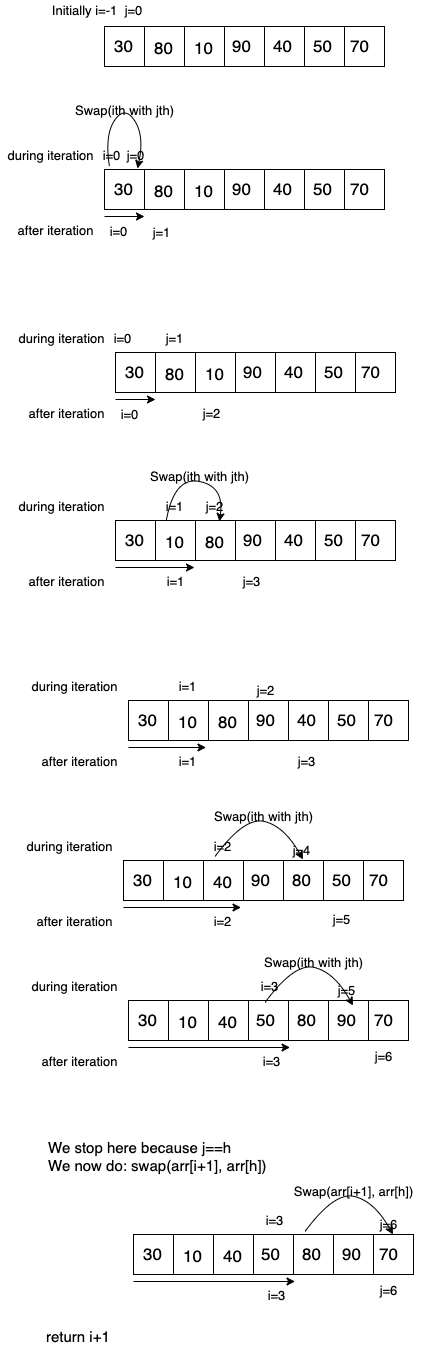
Cornor cases
Dry run yourself:
- {70, 60, 80, 40, 30} ==> No small value than pivot
- {30, 40, 20, 50, 80} ==> No large value than pivot